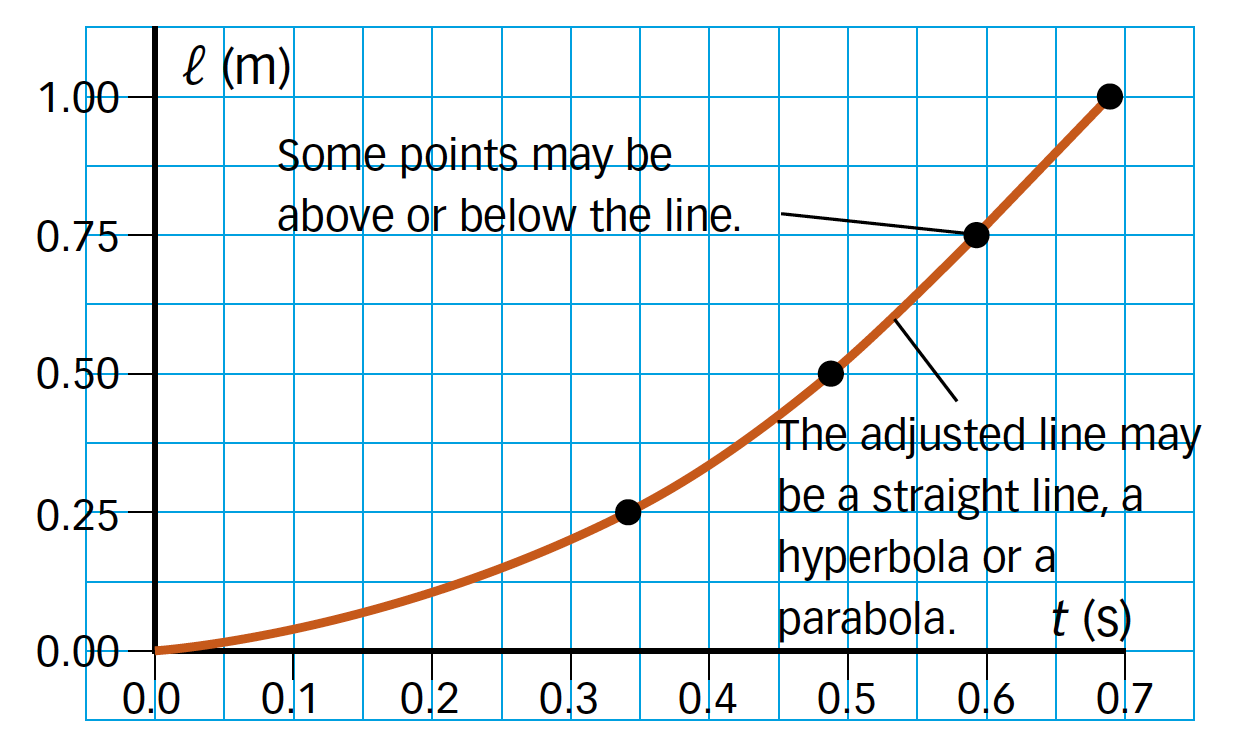
The graphs show the data obtained in a visual way. For example, the graphs show the relationship between two variables and allow us to know values that we have not measured:
- Interpolating data is to obtain intermediate values to other measured ones.
- Extrapolating data is to obtain values outside the range of those that have been measured
For example, for Ball A, a graph like this may be obtained: