The colonial power controlled the foreign policy and wealth of the colonised nation. However, local authorities were in charge of domestic policy. Examples included Britain in Egypt, and France and Spain in Morocco.
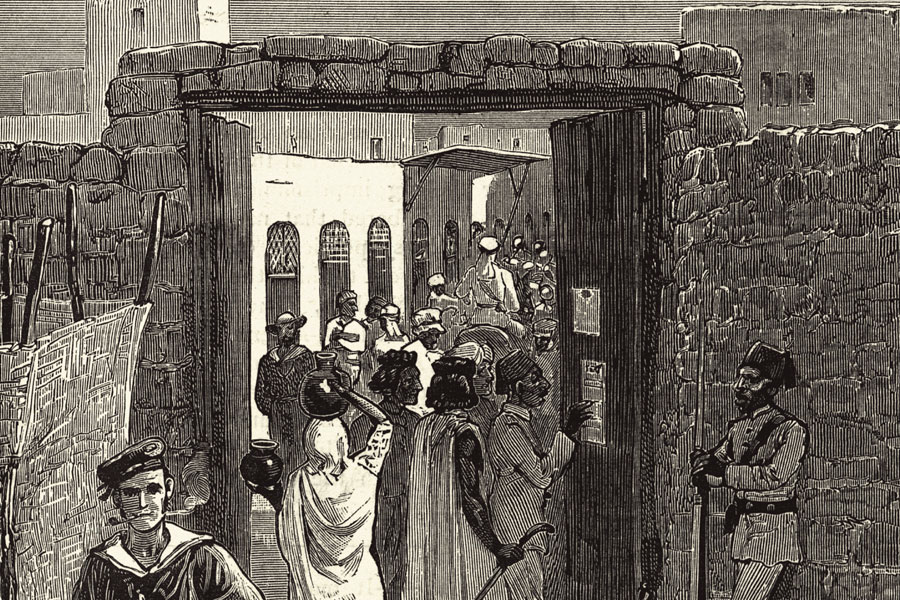
19th-century engraving of people reading the proclamation of the British protectorate in Suakin, Sudan.