We use cookies to improve and analyse your browsing experience on our web. You can accept these cookies, reject them or choose your settings by clicking on the corresponding buttons. Please note that rejecting cookies may affect your browsing experience. For more information you can consult our Cookies policy.
Cookies are an essential part of how our web works. The main goal of cookies is to make your browsing experience more comfortable and efficient and to improve our services and the web itself.
Here you can find all the information about the cookies we use and you can activate and/or deactivate them according to your preferences, except for those cookies that are strictly necessary for the operation of the web. Blocking some cookies may affect your experience on the web and how the site works. For more information you can visit our Cookie Policy.
These Cookies are necessary for the web to function and cannot be disabled on our systems. They are generally only set up in response to actions you may take such as requesting services, setting your privacy preferences, logging in or completing forms. You can set your browser to block or warn you about these cookies, but some parts of the web will not work. Information about Cookies.
These Cookies allow us to count the number of visits and traffic sources so that we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to find out which pages are the most popular and least popular, and to see how visitors move around the web. All information collected by these Cookies is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these Cookies we will not know when you visited our web. Information about Cookies.
These cookies are used to analyse your activity in order to show you personalised advertisements. Information about Cookies.
Change theme

Revision mode

The Cold War had two main phases: an initial phase between 1947 and 1961, during which there was a high level of tension between the superpowers, and a second phase characterised by an easing of tensions between 1962 and 1975.
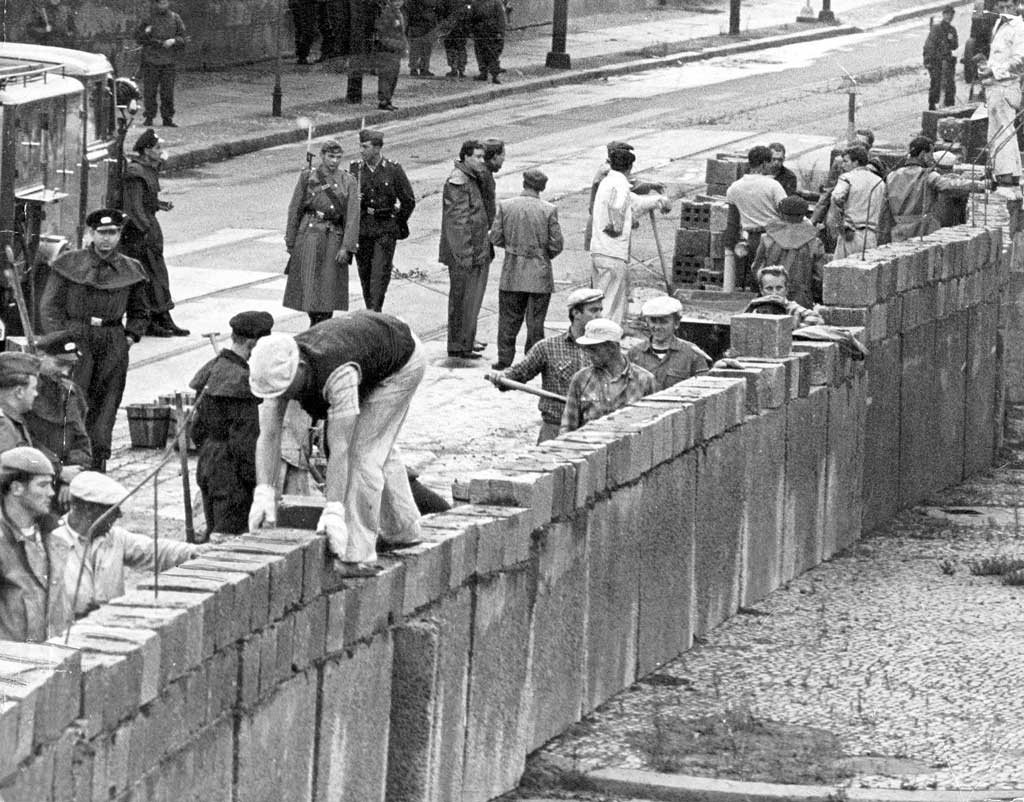


The Berlin Wall
That Sunday morning in 1961, the noise of military vehicles unloading reels of barbed wire and concrete posts disturbed the peace of Berlin and awoke its inhabitants [...] In some sectors the wall ran along the middle of the street so as not to pass through West Berlin, or through the centre of a graveyard. [...]
For the next 19 years the wall was continually reinforced with 3.6 metre concrete blocks that were separate from the original fence, creating a no-man's land' which was under constant surveillance.
The wall separated many families during the Cold War. More than 100000 people tried to cross the wall to escape from East Berlin to West Berlin.
Historia: Del origen de la
civilización a nuestros días,
Pearson (Translated)
|
The Korean War: an unresolved conflict? The Korean War began in 1950 when communist North Korea, which was supported by the USSR and China, invaded South Korea, which was supported by the United States and the UN. The conflict ended in 1953 when an armistice was signed. A demilitarised zone was established along the 38th parallel to separate the two countries. A totalitarian communist regime was established in North Korea, and a republic backed by the United States was set up in South Korea. However, the two countries have never signed a peace treaty.
|
The easing of tensions was caused by two main factors.
After this period of reduced tensions, the Cold War continued until 1991 (when the USSR was dissolved).
The Arab–Israeli Conflict
Following the Holocaust, the UN approved the division of Palestine into two territories in 1947: Palestine, with a Muslim Arab population, and Israel, with a Jewish population.
In 1948 Great Britain's mandate over the area ended and it withdrew. The Jewish population proclaimed the State of Israel, which began the progressive occupation of the Palestinian zones. The Palestinians did not declare statehood because they did not agree with the division of the territories that had been approved by the UN. This situation led to a series of wars between the Israelis and the Palestinians and their Arab allies, including the First Arab–Israeli War in 1948–1949 and the Six-Day War in 1967. This conflict is known as the Arab–Israeli conflict.
In response to the conflict, the United States and Western Europe supported Israel, while the Arab countries (such as Egypt, Syria and Jordan) supported the Palestinians.
Israel's victories in the First Arab–Israeli War and the Six-Day War allowed it to acquire territory in the Sinai Peninsula (Egypt), the Golan Heights (Syria) and Gaza and the West Bank (Palestine). In 1964 the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) was established, and in 1987 the First Intifada began. This was a popular uprising against the Israeli occupation in Gaza and the West Bank.
During the following decades, there were periods of increased and decreased intensity, but the conflict remains unresolved today.
The Cuban Missile Crisis
After Cuba had gained independence, it remained in a semi-colonial relationship with the United States. In 1952 there was a military coup and Fulgencio Batista established a dictatorship.
In 1959 there was a revolution led by Fidel Castro, who established an authoritarian communist regime. In order to try to remove Castro, there was an American-backed invasion of Cuba in 1961 known as the Bay of Pigs, but this ended in failure.
Castro established an alliance with the USSR and in 1962 he allowed the Soviets to place nuclear weapons pointed towards the United States in Cuba. Negotiations between Kennedy and Khrushchev were successful in avoiding an armed conflict. This was the closest the superpowers had come to a direct conflict since the Cold War began.
|
The Vietnam War (1954–1975) After gaining independence from France, Vietnam was divided into two states: North Vietnam, which was a communist state led by Ho Chi Minh, and South Vietnam, which was supported by the Western Bloc. This division was the main cause of the Vietnam War. There were, however, other factors:
The United States sent troops to support the South Vietnamese government in its fight against the Vietcong. It also carried out massive bombing campaigns of North Vietnam and some areas of South Vietnam. However, despite this the United States was unable to defeat the Vietcong.
In 1969 President Richard Nixon began to withdraw American troops from Vietnam, although he continued to support South Vietnam. In 1973 a peace settlement was signed, but in 1975 North Vietnam took control of South Vietnam and reunified the country as a communist state. In effect the United States had been defeated. Around the same time, Vietnam's neighbours, Laos and Cambodia, also became communist states. The Vietnam War had serious consequences for the United States.
DIFFERENCES OF OPINION WITHIN THE UNITED STATES ABOUT THE VIETNAM WAR [...] The fight against communism should be brought to South-East Asia with strength and determination in order to achieve victory [...] The country (Vietnam) can be saved if we act quickly and with prudence. We must decide whether to support Diem (the President of South Vietnam) [...] or allow Vietnam to sink [...] (Lyndon B. Johnson, President of the United States) [...] Help stop the murder of American youth. More than 7500 have already been killed in order to protect a corrupt military dictatorship, which has been kept in place against the wishes of the Vietnamese people. Help stop the merciless bombing of men, women and children. Help stop the use of the incendiary napalm, gases and toxic chemicals which destroy harvests in a country already suffering from poverty. Help stop the loss of thousands of millions of our dollars in Vietnam. Help bring our children home. (Appeal of American educators, March 1967) A. León Conde, Guerras del siglo XX, Salvat (Adapted and translated) |
Activity 26
Remember
Actividad 27
Understand
Activity 28
Listen and answer the questions about the Berlin Blockade.
Activity 29
Apply
Activity 30
Evaluate
Activity 31
Understand
Activity 32
Write a summary of the Vietnam War in your notebook, including:
Activity 33
Apply
Activity 34
Evaluate
Activity 35
Find out more about the intifadas. Write a short essay including their causes, who the uprisings were directed against, the forms they took and the population groups that participated.